Data is an important asset to any organization. Attackers located all over the world try to get a hold of this data for ransom, to sell, or simply to gain leverage over a company. Therefore, such data should be handled securely within an organization to ensure that its confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) are kept intact.
To do so, organizations need to adopt and adhere to data security standards that aim to accomplish CIA within an organization.
This blog will explore the essentials of data security standards and some of the most used data security standards around the world.
What Are Data Security Standards?
Data breaches have been at an all-time high, with the average cost per incident hitting a staggering $4.45 million in 2023. In response to the increasing threat to data security, numerous data security standards have been introduced across multiple industries that sometimes focus solely on protecting industry-specific information such as health, payment cards, or Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
These security standards are best practices on how organizations can protect their data while ensuring that it is not subject to unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or any other action that significantly impacts the organization.
Importance of Data Security Standards
Modern data security standards are used by organizations for many reasons, some of which include:
- Protecting sensitive information: Safeguarding customer data, financial records, and intellectual property from breaches and unauthorized access.
- Compliance and legal requirements: Meeting stringent regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS to avoid penalties and build trust.
- Building trust and reputation: Demonstrating commitment to data protection, enhancing customer trust, and improving reputation.
- Enabling business opportunities: Facilitating partnerships and growth by meeting industry standards.
- Staying ahead of threats: Adapting to evolving cyber threats with updated security protocols.
Major Data Security Standards
Numerous data security standards are in use today, providing organizations with guidelines and best practices to protect sensitive information.
This section explores some of the major data security standards that play a critical role in safeguarding data integrity, confidentiality, and availability across different industries and sectors.
ISO/IEC 27001/27002

ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management System (ISMS)
ISO/IEC 27001 establishes the requirements for implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS) within an organization. Key aspects include:
- Risk management: Identification, assessment, and treatment of information security risks tailored to organizational needs.
- Control objectives: Setting clear security objectives and selecting controls to mitigate identified risks.
- Continuous improvement: Establishing processes for ongoing monitoring, review, and improvement of the ISMS.
ISO/IEC 27001 certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to managing information security risks systematically and protecting sensitive data assets.
ISO/IEC 27002: Code of Practice for Information Security Controls
ISO/IEC 27002 complements ISO/IEC 27001 by providing a detailed set of best practices and controls for implementing information security. Key areas covered include:
- Access control: Restricting access to information assets based on business requirements.
- Cryptography: Protecting data through encryption, key management, and cryptographic protocols.
- Physical and environmental security: Safeguarding physical premises, equipment, and supporting infrastructure.
- Incident management: Establishing procedures for detecting, reporting, and responding to security incidents.
Organizations use ISO/IEC 27002 as a practical guide to select and implement appropriate security controls aligned with their specific risks and operational contexts.
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)

PCI-DSS is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data during debit, credit, and prepaid card transactions.
Some Key Requirements Include:
- Secure network: Maintain firewall protection and secure configurations.
- Data protection: Encrypt cardholder data during transmission and storage.
- Vulnerability management: Regularly update systems and applications.
- Access control: Restrict access to cardholder data based on business need-to-know.
- Monitoring and testing: Monitor network access and conduct regular security testing.
- Information security policy: Develop and maintain a comprehensive security policy.
Some compliance and benefits include:
- Compliance requirements: Mandatory for organizations handling cardholder data.
- Security enhancement: Protects against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Trust and reputation: Builds customer trust and meets regulatory obligations.
- Cost savings: Reduces risks and financial liabilities associated with data breaches.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)

HIPAA is a U.S. legislation ensuring the security and privacy of patient health information.
Some key components include:
- Privacy rule: Protects individually identifiable health information (PHI) held or transmitted by covered entities.
- Security rule: Sets standards for securing electronic protected health information (ePHI) through administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
- Breach notification rule: Mandates reporting breaches of unsecured PHI to affected individuals and regulatory bodies.
- Enforcement rule: Establishes penalties for violations and enforcement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Some compliance and benefits include:
- Compliance: Required for healthcare providers, plans, and clearinghouses handling PHI.
- Benefits: Enhances patient trust, ensures legal compliance, improves data security, and streamlines healthcare operations.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)

The GDPR is a comprehensive EU regulation aimed at enhancing data protection and privacy for individuals within the EU/EEA and regulating the export of personal data outside these regions.
Some key principles include:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Data must be processed lawfully, fairly, and transparently.
- Purpose limitation and data minimization: Data collection must have clear purposes, and data collected should be limited to what is necessary.
- Accuracy, storage limitation, and security: Data must be accurate, kept for no longer than necessary, and protected with appropriate security measures.
Compliance requirements with GDPR include:
- Organizations processing EU/EEA personal data must comply with GDPR’s requirements, including data protection assessments and notifying breaches.
- GDPR grants rights such as access, rectification, erasure, data portability, and objection regarding personal data.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
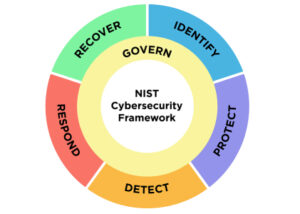
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) by the National Institute of Standards and Technology provides voluntary guidelines and best practices for organizations to manage and improve their cybersecurity risk management processes.
Some core components of this framework include:
- Framework core: Includes five functions- identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover-each with specific categories and subcategories outlining cybersecurity activities.
- Implementation tiers: Provide context on organizational cybersecurity risk management practices ranging from Partial (tier 1) to Adaptive (tier 4).
- Framework profile: Helps organizations align cybersecurity activities with business objectives, risk tolerance, and resources.
Some benefits of implementing NIST CSF include:
- Risk-based approach: Prioritizes cybersecurity efforts based on risk assessment and business needs.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to different sectors, sizes of organizations, and regulatory requirements.
- Continuous improvement: Supports ongoing refinement and enhancement of cybersecurity practices.
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)

SOC 2 is a framework designed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) to help service organizations manage data security and privacy concerns. It focuses on controls relevant to the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data.
Some key components of SOC 2 include:
- Trust service criteria: Includes security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy principles.
- Report types: Type I (design) and Type II (operational effectiveness) reports.
- Scope: Determined by the services provided and applicable trust service criteria.
Some benefits of implementing SOC 2 include:
- Customer assurance: Demonstrates commitment to data security and privacy standards.
- Risk management: Identifies and mitigates risks associated with data handling.
- Competitive advantage: Sets a standard for data protection, enhancing trust and marketability.
- Regulatory alignment: Assists in meeting regulatory requirements related to data privacy and security.
Other Relevant Standards and Frameworks
In addition to the popular standards mentioned above, other standards also aim to improve data security within organizations. These standards and frameworks include:
- CIS Controls: The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls are a set of cybersecurity best practices designed to help organizations prioritize and implement basic cyber defense measures. They are organized into three categories: basic, foundational, and organizational controls, focusing on essential security actions that mitigate prevalent cyber threats.
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): COBIT is a framework developed by ISACA for IT governance and management. It provides a set of controls and best practices to align IT objectives with business goals, including frameworks for managing risk, ensuring compliance, and optimizing IT resources.
- CSA Security Guidance: The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Security Guidance offers best practices and security controls for cloud computing environments. It addresses a wide range of security concerns, including data protection, identity management, compliance, and incident response in cloud environments.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing cybersecurity standards and frameworks is critical for organizations that want to strengthen their defenses against the latest cyber threats and protect sensitive information.
However, implementing a security framework isn’t simple. You may encounter many challenges that vary from resource constraints and technological complexities to regulatory restrictions and talent shortages.
So, here are some challenges that you might run into while implementing security standards.
1. Resource Intensity
Implementing data security standards and frameworks often requires significant resources, including financial investment, dedicated personnel, and time commitment. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may find it particularly challenging to allocate sufficient resources for compliance.
2. Complexity
The complexity of data security standards and frameworks can be scary, especially for organizations with limited technical expertise or mature data security programs. Understanding and effectively implementing detailed controls and requirements may require specialized knowledge and training.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Aligning data security standards with existing IT infrastructure and systems can pose challenges. Organizations may need to modify or upgrade their current technology stack to meet the framework’s requirements, which can be costly and disruptive.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Maintaining compliance with data security standards is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and updates. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, updating security controls, and promptly addressing emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
5. Skills and Expertise Gap
Finding and retaining skilled data security professionals capable of implementing and managing complex standards and frameworks is a significant challenge. The global shortage of data security talent exacerbates this issue, making it difficult for organizations to build and maintain robust data security programs.
Wrapping Up
Implementing data security standards and frameworks is crucial for protecting organizations against cyber threats and safeguarding sensitive data.
Despite challenges, these efforts are essential for enhancing security, complying with regulations, and earning stakeholder trust. By prioritizing data security, organizations can build a resilient defense against evolving threats and ensure long-term resilience in the digital landscape.