Data is a crucial part of any organization, especially in an enterprise. Data is now at the heart of any operation and business process, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and deal with numerous customers from across the globe.
There lies one of the main challenges for enterprises dealing with data: an enterprise is responsible for whatever data is captured, processed, or stored. This could be data that belongs to their employees, customers, or partners.
With global data protection and security regulations such as GDPR and ISO 27701 requiring strict and secure management of data, it is paramount that enterprises understand the importance of data encryption.
Breaking Down Data Encryption
Whenever data encryption needs to be implemented, enterprises need to consider the following forms of data:
- Data at rest
- Data in motion
- Data in use
Data at rest refers to the requirement of encrypting all data when it is stored. This means encrypting disks, storage volumes, databases, or even the actual data. The level of data encryption necessary must always be determined according to the enterprise’s requirements and risk appetite.
Data in motion looks at securing the data when it is being transferred from one place to another, such as from a client to the server. In this case, the communication channels must be secured appropriately using secure protocols and other mechanisms.
Data in use looks into securing the data when it is being processed. This usually involves the use of specialized encryption mechanisms such as homomorphic encryption that enables computation on encrypted data, therefore never exposing the raw data.
Implementing Enterprise Data Encryption
Encrypting data sounds simple, but there needs to be special consideration when implementing data encryption at the scale at which enterprises operate and the sheer amount of data that they process and store.
Here are some of the crucial aspects that need to be considered when implementing enterprise data encryption:
1. Encryption Protocols and Standards
It’s easy to get carried away and use the strongest encryption algorithms to secure all the data within an enterprise. Even though this can make the data secure, it will not fit the requirements of the business in terms of efficiency and performance.
Therefore, using the correct protocol, standard, and algorithm for each type of requirement is crucial for balancing the overall security and the usability of the data.
2. Key Management Strategies
In an enterprise, there will be numerous keys that are required to encrypt resources such as databases and volumes. Managing the lifecycle for each of these keys is challenging without the right tools and strategies.
Therefore, it is important to define the key management policies and procedures beforehand depending on the business and compliance requirements and later deploy the right technical solutions to carry out agreed-upon requirements.
There are many approaches an enterprise can take, however; having a proper solution will make or break the strategy. Therefore, having a comprehensive and scalable solution such as the AWS KMS (Key Management Service) enables enterprises to manage, rotate, and securely store hundreds or thousands of keys across a complex environment with little to no effort.
Additionally, there are options where the enterprise could allow a cloud service provider to manage their keys for specific supported services. One such method is AWS-managed keys, where some parts of the key lifecycle can be offloaded, thus easing the workload of the teams maintaining the systems.
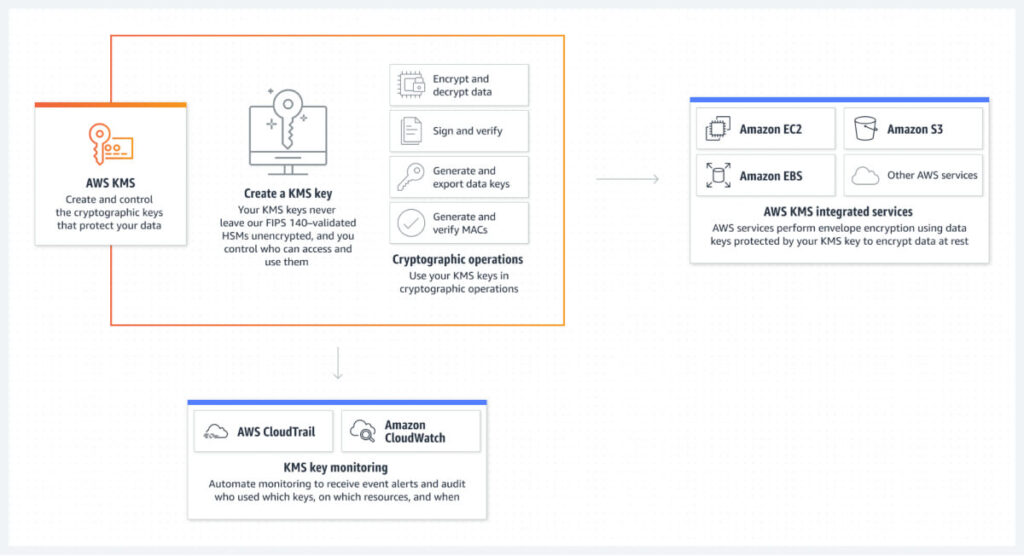
3. Encryption Deployment Strategies
Encrypting a wide array of data across numerous resources is not a simple task. Therefore, specific deployment strategies must be created to ensure consistency across the enterprise.
- Centralized vs. decentralized encryption: Evaluating how the deployment will take place will depend on what is necessary to meet the business requirements and also to ensure there is room for future enhancements.
- Cloud encryption: Encrypting data in the cloud is completely different from encrypting data stored in local data centers. It is crucial to evaluate the efficiency, capability, and costs involved in using cloud-native encryption mechanisms to encrypt data in the cloud.
- Endpoint encryption: Each piece of data will flow through an endpoint at some point. These endpoints can be laptops, mobile devices, or even IoT devices. It is crucial that encryption technologies support every endpoint used within the enterprise to ensure that no data is unprotected.
- Database encryption: Implementing encryption at a database level can prevent unauthorized access and data breaches; however, if not done right, it could hinder the performance of the entire database and any applications connected to it. Therefore, determining a strategy that takes into account the level of encryption necessary for each type of database is crucial.
Data Peace Of Mind
PVML provides a secure foundation that allows you to push the boundaries.

4. Integration With Existing Infrastructure
New encryption strategies and technical controls must be versatile and compatible with any existing infrastructure that may be running within an organization. Practically any enterprise running for more than 10 years could have some type of infrastructure that is outdated and cannot be replaced for various reasons. Implementing state-of-the-art encryption on outdated infrastructure would be challenging and could sometimes even break the entire solution.
Therefore, these aspects of the infrastructure must be taken into consideration when designing an encryption strategy while ensuring that all infrastructure can be included in the deployment.
Challenges and Risks
There are always issues that can come up during the deployment of any enterprise encryption solution; being prepared is the only way around them.
Here are some challenges and risks that could affect the enterprise while rolling out enterprise data encryption:
- Key management complexity: Key management will become more complex as the number of systems increases within an enterprise. Therefore, having proper mechanisms to manage each key is paramount.
- Performance impact: Encryption always comes with a trade-off from performance; therefore, it is necessary to determine the maximum performance impact that an enterprise is willing to take to implement data encryption.
- Compliance and regulatory requirements: Inadequate data encryption could leave the enterprise with serious compliance and regulatory fines for noncompliance. Therefore, always understanding the requirements before deploying a solution is crucial to ensure all compliance and regulatory requirements are met.
- Insider threats: There’s always a risk from insiders to any enterprise. Managing these risks when implementing an enterprise data encryption strategy marks the hallmark of a successful deployment. Having role-based access to encryption keys and resources, as well as maintaining segregation of duties, lays the groundwork for an enterprise to maintain a zero-trust approach to its practices.
Wrapping Up
It is important to understand the crucial role that data encryption plays within an enterprise and how a well-thought-out strategy can be the difference between success and failure in deployment.
When deploying data encryption across an organization, there may be fundamental issues with the technologies and strategies due to the sheer scale of the enterprise. It is important to understand that there is no silver bullet for enterprise data encryption and that each strategy must be designed and fine-tuned according to the business requirements.