What is Data Security Governance?
For companies that deal with sensitive data, it’s important to have an overall management process that’s implemented to ensure the security of the sensitive data in the company.
This is exactly what data security governance provides to an organization.
The data security governance framework provides an overview of policies, standards, technologies, and controls that protect critical data from being compromised. A mature framework aims to remove the misconception that security should be handled at the upper level. It engages stakeholders of all levels in the organization to ensure that security and risk management are a coordinated priority.
But, when implementing a data security governance framework, it’s important to consider a few security principles to create a strong, refined process.
Data Security Principles
All data processed in an organization is bound to the following principles:
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
- Authorization
- Authentication
- Accountability
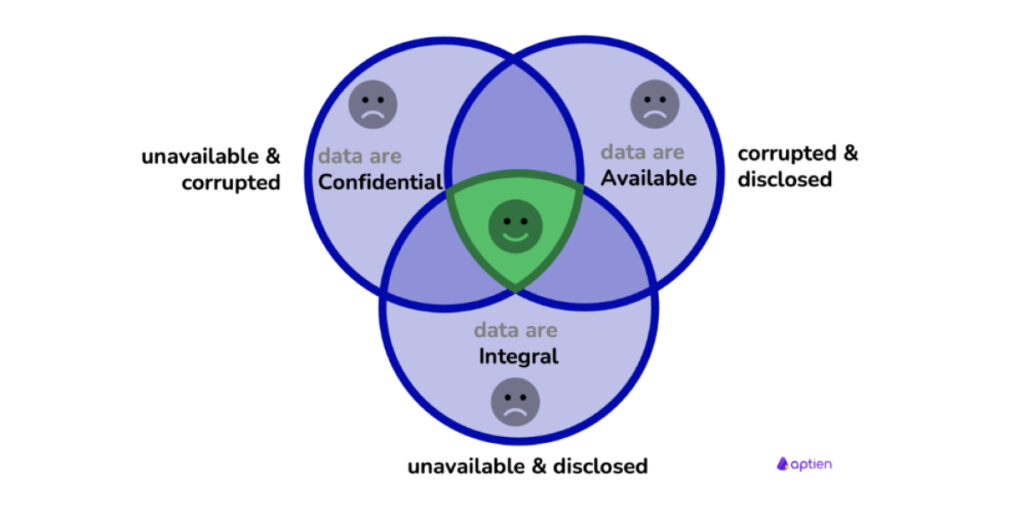
Source: https://aptien.com/en/kb/articles/what-is-cia-triad
As shown above, these three principles form a perfect triad (CIA Triad) where data is most secure when all three parameters are met.
Confidentiality
This means that data should only be accessed by the authorized member, thus ensuring that data cannot be misused.
Integrity
This means that the data that you process will be delivered to the end user without any intervention, thus indicating that the data is authentic and trustworthy.
Availability
This means that a user can get data from a system at any given time that is required.
Additionally, it’s important to look at the triple A triad (AAA).
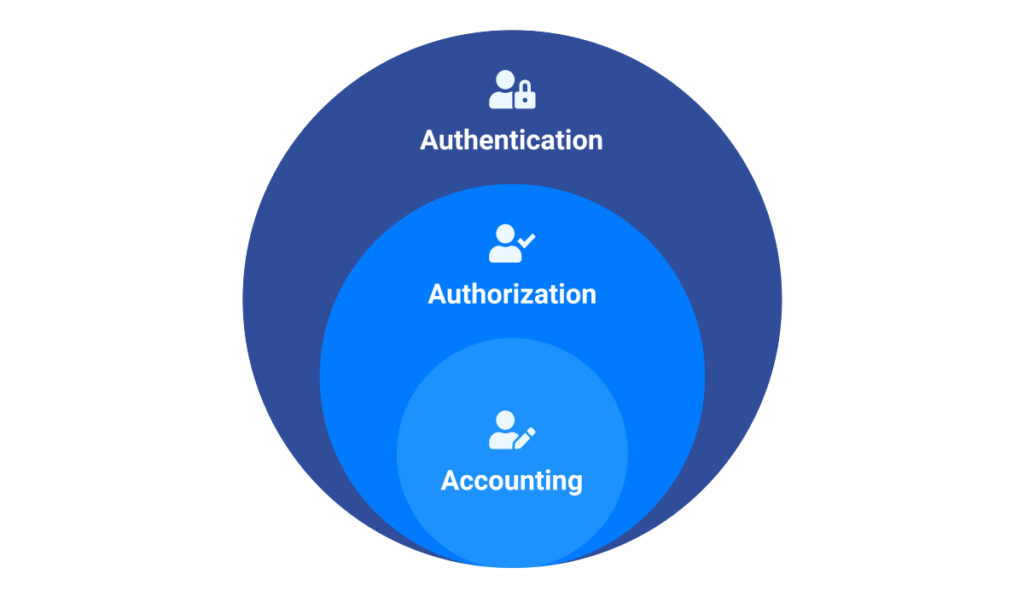
The AAA Triad is a three-process framework used to manage user access, enforce user policies and privileges, and measure the consumption of network resources.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of identifying a user and granting them access to the network. This ensures that only users with the right credentials can gain access to a system.
Authorization
Even if a user is authenticated in a system, it doesn’t mean they should gain access to data. Instead, there needs to be right authorization mechanisms in place to do so. This means that only intended users should get access to their data.
Accounting
When users navigate through data in your organization, it’s important to keep track of the data they accessed and for what purpose. This can be broken down into:
- Why: Why did the user access the data?
- What: What did the user access?
- When: When did the user access the data?
- Where: Where was the user located when accessing the data?
- How: How did the user access the data? Was it through a laptop or a mobile?
Answering these questions helps build a strong audit trail around the data, ensuring that steps can be traced back in case of a breach.
Therefore, it’s important to understand that a robust data security governance framework must consider data security principles to ensure that the right procedures are implemented.
Data Peace Of Mind
PVML provides a secure foundation that allows you to push the boundaries.

How To Create a Data Security Governance Framework?
Now that you understand the factors to consider when building a framework, it’s important to understand how to build a framework.
This can be broken down into a series of steps:
Step 01: Establish a data governance committee
First, form a committee of executive stakeholders from IT, security, legal, finance, and key business units. Define the committee’s charter, responsibilities, and decision-making authority. Schedule regular meetings to review security posture and initiatives.
Step 02: Classify your data
Document all critical data types and locations. Analyze data sensitivity, value, and regulatory exposure. Classify data into risk levels based on findings. Define approved handling in policy for each classification.
Step 03: Develop data security policies
Start with an endorsed overall data security policy. Create specific policies aligned to data governance frameworks for data classification, retention, data access control, and more. Address data access management through roles, responsibilities, acceptable use, decentralized access control, and self-service processes.
Step 04: Conduct risk assessments
Inventory assets, flows, controls, and vulnerabilities. Evaluate probability and business impact for identified risks. Prioritize mitigation based on risk ratings. Generate reports based on assessments to inform security roadmaps.
Step 05: Implement safeguards and controls
Deploy data security controls per policies. Use platforms to automate controls and monitoring. Perform testing to validate effectiveness.
Step 06: Develop incident response plans
Define roles, playbooks, and communications protocols for incident responses. Tailor plans for data breach scenarios. Test via exercises to find gaps.
Step 07: Provide training and awareness
Educate all on security policies and procedures. Reinforce the policies and procedures to users with phishing simulations and compliance testing. Post awareness materials and tips continuously.
Step 08: Perform audits and monitor activity
Schedule routine internal and third-party data audits. Actively monitor systems and users for violations. Refine controls and policies based on findings.
Step 09: Review and report regularly
Revisit policies and controls for improvements. Update programs for new threats and regulations. Report progress and metrics to leadership.
Technology and Tools for Data Security Governance
Implementing a robust data security governance framework requires not just policies and procedures but also the strategic use of technology solutions. These tools are essential for enforcing the framework’s policies, detecting and responding to threats, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Some tools and technologies to consider when implementing this framework includes:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools are designed to prevent unauthorized access and transfer of sensitive information outside the network. They can identify, monitor, and protect data in use (e.g., endpoint actions), in motion (e.g., email, IM, web traffic), and at rest (e.g., data storage) through deep content analysis and real-time monitoring.
- Encryption Software: Encryption is fundamental for protecting data confidentiality and integrity. Encryption software can secure data at rest (e.g., on servers, databases, laptops) and in transit (e.g., data being transferred over the network). It ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable and secure.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM systems provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. They aggregate and correlate data from various sources, identify deviations from the norm, and initiate responses to mitigate threats. This is crucial for early detection of data breaches and compliance monitoring.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM systems ensure that only authorized individuals can access certain data or systems. They manage user identities, their authentication, and authorization for accessing resources. This includes single sign-on systems, multi-factor authentication, and privileges management.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: These platforms collect, aggregate, and analyze information about emerging threats from various sources. They help organizations stay ahead of potential security threats by providing actionable intelligence and enabling proactive defence strategies.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): CASBs give organizations visibility into their cloud services usage and provide granular control over data access and movement. They help enforce security policies in cloud environments, assess risk, and protect against threats.
Benefits of Implementing a Data Security Governance Framework
By implementing a strong, matured framework, it offers benefits such as:
- Risk management: The framework will align security with business goals and risk tolerance. This means that security will be brought as the forefront of the business and will not be considered an afterthought.
- Unified control: It centralizes control over dispersed security efforts.
- Establishes standards: It enforces established data protection standards across systems.
- Data visibility: It improves visibility into data risks and identifies compliance gaps.
- Awareness and responsibility: It promotes security awareness by providing all users with defined security standards and establishes shared responsibility models.
- Adaptability: It creates processes to adapt security as threats and regulatory obligations evolve.
Wrapping Up
A data security governance framework is essential for any organization handling sensitive data. By prioritizing data security governance, organizations can not only protect their valuable data assets but also build trust with customers, stakeholders, and regulators.
Therefore, it’s important to follow the steps outlined in this article and consider the technologies listed to build an effective data security governance framework while considering the data security principles, to help build a strong framework that can significantly improve the data security within an organization.