Introduction
PII, or Personally Identifiable Information, is the information that can either directly or indirectly identify an individual. Information considered within this category can be vast; however, the following list encompasses a sample of the most common information that is categorized as PII:
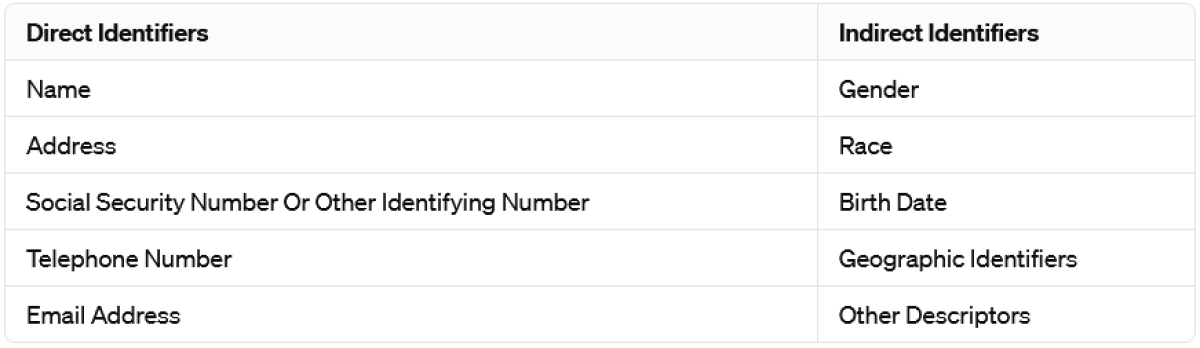
Many regulations aim to protect PII and restrict its use for intended purposes only; therefore, PII must be handled and managed in an acceptable form without exposing too much sensitive information.
This can be achieved in many ways; the most common method is to mask or anonymize the PII by replacing or obscuring the information so that only part of the PII is visible to the users.
Understanding PII Masking
PII masking aims to obscure sensitive information, ensuring it remains indecipherable to unauthorized parties while retaining functional integrity. Unlike data encryption, where the data is rendered unreadable without the decryption keys, PII masking focuses on replacing or modifying PII with synthetic or randomized values.
The Risks of PII Exposure
Nowadays, numerous regulations and frameworks mandate the protection of PII to protect individuals when using digital systems or even operating in different geolocations.
Regulations such as GDPR enforce substantial fines that can exceed a billion dollars. With these tight regulations in place, organizations need to stay on top of their data protection standards more than ever to ensure they operate within regulatory standards.
Even though fines can be significant, there are other risks that organizations go through during a PII exposure. Most organizations will suffer reputational damage that will cause customers to lose faith and trust in the company to manage PII, leading to significant, unaccountable financial losses.
These damages may even affect future business that organizations try to secure due to their poor track record with PII protection.
Benefits of PII Masking
There are many benefits to implementing PII masking within an organization. These can range from short-term benefits, such as enhanced privacy protection, to long-term financial benefits.
The following are some of the most common benefits that organizations can see with the implementation of PII masking:
- Enhanced privacy protection: PII masking enhances privacy by safeguarding sensitive information and minimizing the risk of identity theft, fraud, and other privacy breaches by replacing or obscuring PII values.
- Preservation of data utility: Unlike encryption, which renders data unreadable, PII masking maintains data usability while ensuring privacy. This enables organizations to leverage data for analytics, testing, and collaboration without compromising privacy or regulatory compliance.
- Reduced risk of data breaches: PII masking minimizes the risk of data breaches by making sensitive information less appealing to malicious actors. Masked PII is less valuable for identity theft or fraud, minimizing the impact of breaches on individuals and organizations.
- Compliance with data protection regulations: In today’s regulated environment, compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA is crucial. PII masking ensures sensitive information is protected, aiding organizations in meeting compliance requirements and avoiding regulatory penalties.
- Maintaining trust and reputation: Data breaches and privacy violations can harm an organization’s reputation. Implementing PII masking demonstrates a commitment to customer privacy, fostering trust, enhancing brand reputation, and boosting competitive advantage.
- Cost-efficiency: Data breaches and privacy violations result in substantial financial costs. PII masking reduces these costs by lowering the likelihood and impact of breaches. Investing in robust data protection minimizes potential financial repercussions.
- Facilitates data sharing and collaboration: PII masking facilitates secure data sharing and collaboration among teams, partners, and vendors. Anonymizing or pseudonymizing sensitive data allows for freer data sharing while preserving privacy and security, promoting collaboration and innovation.
Implementing PII Masking
In many cases, implementing PII masking within a large-scale organization has its own challenges. However, following the main focus areas below will provide a foundation to start masking PII.
- Assess the data: Begin by identifying the categories of PII existing in your datasets and systems. Determine where sensitive information is stored and the level of risk associated with each data element.
- Select masking techniques: Choose masking strategies that are appropriate for the nature of the data and the individual use cases. When deciding on masking strategies, take into account data format, storage systems, and regulatory requirements.
- Integrate with existing systems: Ensure that PII masking strategies integrate seamlessly with existing data management and security systems. This may include customizing or configuring software tools and platforms to meet masking requirements.
- Test and validate: Implementations of PII masking should be thoroughly tested and validated to verify their effectiveness and correctness. Test various situations and data sets to discover potential faults or unexpected repercussions of masking.
- Data quality and usability: Find a balance between data privacy and usability by evaluating the effect of masking on data quality and usefulness. Monitor data integrity after masking and make any required changes to ensure usefulness while safeguarding privacy.
- Training and awareness: Provide training and awareness programs for staff who are involved in PII masking processes. Ensure that employees understand the importance of data privacy and their responsibilities in successfully using masking strategies.
- Documentation and compliance: Maintain complete documentation of all PII masking operations, including masking rules, algorithms, and settings that will help to comply with applicable data protection requirements such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement: Implement systems for continuous monitoring of PII masking operations to detect abnormalities or security issues. Continuously enhance masking tactics and processes in response to feedback, audits, and changing threats.
- Vendor selection and oversight: When using third-party providers for PII masking solutions, thoroughly assess them and verify they follow strict security and privacy guidelines. Establish explicit processes for monitoring vendor performance and compliance.
Wrapping Up
There are many different approaches to PII masking. It is crucial to understand that there is no silver bullet for all organizations and use cases. Many organizations may even need to develop their own methodologies and strategies to achieve their PII masking requirements.
However, organizations can follow the same PII masking strategies for common PII, such as social security numbers, telephone numbers, email addresses, and names that may be found within the organization and its processes.
Organizations must understand that PII masking cannot be rolled out overnight, and if this method is used, many business processes may be affected and rendered unusable. Therefore, the optimum method to roll out PII masking is to take a staged approach, where each identified process and data type is taken one at a time. This will reduce the issues that PII masking would bring out and make it easier to deal with.