Understanding Sensitive Data
Whether you like it or not, every single organization will contain some sort of sensitive data. Back in the day, these used to be filed safely in vaults that only a limited number of people had access to, but with the introduction of new technology and its vast adoption, almost every company is moving to a digital-first approach where these traditional files are converted into data stored either on physical servers or even in the cloud.

You may be asking yourself, but what exactly is the sensitive data that my company has?
This is quite simple to answer. Sensitive data is any type of data that holds a significant value to an individual, organization, or entity that, if compromised, could lead to significant harm to privacy, security, financial well-being, or reputation.
Here are a few popular examples of what can be labeled as sensitive data:
- Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
- Financial Information
- Health Records
- Intellectual Property
- Trade Secrets
Looking back at the recent data breaches that took place over the past few years, such as those at Boeing, Okta, and many other data breaches that leaked thousands if not millions of records, we can see significant impacts on the entities and even the entities that are related.
For instance, if you take a look at Okta, it suffered a major data breach in October 2023 in which its support case management system was accessed by a threat actor using stolen credentials. Upon investigation, it was found that the attacker exploited a service account stored in the system itself that had permissions to view and update customer support cases. It was said that an employee had signed in to their personal Google profile on Google Chrome via their Okta-managed laptop, which allowed the attacker to gain access to the service role.
Therefore, with attacks like this impacting several other companies, they tend to create adverse effects on organizations such as:
- Financial Loss
- Reputational Damage
- Identity Theft
- Loss of Trust
- Operational Disruption
What is Sensitive Data Protection?
Now that we know what can happen if any type of sensitive data is compromised, let’s look at what we can do to prevent your sensitive data being compromised.
First, you must understand that the process of protecting sensitive data is called sensitive data protection, and it can take various shapes and forms.
Sensitive data protection fundamentally refers to the measures, practices, and technologies used to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
This can be summarized as protecting the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability of sensitive data.

In a world where data is more valuable than oil, it is not surprising that proper data protection has a significant impact on an organization.
More often than not, many industries refer to data protection as vital to their business. This is because with data protection comes the trust and confidence of the customers in the brand, resulting in more customers and revenue.
Data Peace Of Mind
PVML provides a secure foundation that allows you to push the boundaries.

5 Best Methods for Protecting Sensitive Data
Since data protection plays such a vital role in a business, let’s look at some of the most popular ways to protect sensitive data.
- Data encryption
- Access control and user permissions
- Regular data audits and monitoring
- Employee training on data security
- Data anonymization
Data Encryption
Encrypting data has been one of the most fundamental ways of protecting sensitive data from prying eyes. Encrypting data ensures that the data is no longer readable without the specific key to unlock the data.
Data can be encrypted at rest, in motion, and in use. This means that the sensitive data is never left exposed during its lifecycle and ensures that only authorized personnel can read or use it.
Encryption at rest refers to encrypting the data when it is stored. Typical techniques that we can use to ensure data encryption at rest are full disk encryption, database encryption, or even cloud storage encryption.
When data is in motion, the objective is to set up and use a secure channel to communicate with all parties involved. This means that techniques such as transport layer security (TLS), virtual private networks (VPNs), and secure protocols can be used to secure the communication channel, thus preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
Encrypting data in use is a different challenge where the data must be usable while being protected. Clever techniques such as Homomorphic Encryption enable computations to be performed on the data without it being decrypted. Another technique often used is secure enclaves, where the execution environments are protected using hardware-based security controls so that the data is used within a secure environment.
Access Control and User Permissions
The most fundamental principle of data protection is if the data is inaccessible to an attacker, then the data should remain safe. This is true most of the time, and therefore, principles such as the principle of least privilege and zero trust have been introduced to ensure that all users and entities only get the bare minimum access to do their tasks and nothing more.
This ensures that the attack surface is significantly reduced. Practically implementing these principles is a journey; however, the stepping stones to this journey are access controls and fine-grained user permissions.
Services such as the IAM service within AWS allow users to restrict access to specific resources, thus allowing administrators to provide only fine-grained access rather than allowing users to access all the data. For example, if a user only needs read access to a specific file within a folder, the permissions should only allow this user to read the specific file and nothing more, not even read files within the same folder.
Continuous evaluation of access rights and not trusting an entity-based trust alone reduces the chances of credential misuse and possible attacks launched by attackers. For example, access must be verified and continuously evaluated even if the user is accessing a specific resource from inside the corporate network; there shouldn’t be an implicit trust granted for all access that comes from within the corporate network.
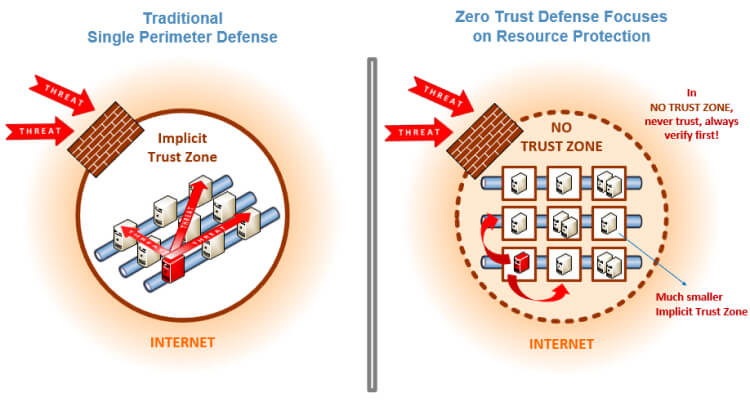
Reference: https://www.nist.gov/blogs/taking-measure/zero-trust-cybersecurity-never-trust-always-verify
Regular Data Audits and Monitoring
No amount of security audits can be enough! This is the bitter truth that all organizations must accept since audits act as the third line of defense for keeping any attacks at bay.
Regular audits ensure that all aspects of data protection, including the policies, procedures, and technical controls, are compliant and effectively protect sensitive data.
Internal or external audits ensure that organizations adhere to the defined standards, industry best practices, or regulatory requirements by conducting these audits periodically, thus highlighting any gaps or non-compliances that may have been present at the time of the audit.
Since audits are carried out periodically, there is a chance that issues or malpractice can occur between these audit cycles. This is where continuous monitoring helps organizations stay on top of all the actions and transactions that are performed on their sensitive data by monitoring the access and the actions carried out by their users, third parties, and anyone of interest.
Continuous monitoring usually happens as a part of the SOC (Security Operations Center), where trained specialists monitor and analyze every single log and metric, trying to identify malicious behavior or suspicious patterns.
Employee Training on Data Security
Investing millions of dollars into state-of-the-art technologies will mean nothing if the employees aren’t trained on data security and how they can secure their data. For example, having a data classification mechanism within the organization will not do any good if the employees aren’t trained on how to effectively use the classification labels.
Furthermore, it’s essential to address the insider threat, which encompasses both malicious intent and negligent actions by employees. Without proper training, employees may unknowingly expose sensitive data or fall victim to malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities within the organization.
Having well-trained staff will not only help organizations make the most out of the technologies they implement but also enable employees to detect malpractices and potential risks, including insider threats. By instilling a culture of vigilance and providing employees with the knowledge and tools to identify and respond to security threats, organizations can reduce the likelihood of data breaches and protect sensitive information.
Turning your employees into human firewalls should be marked down as one of the most crucial areas that every security team must look into. Through comprehensive training programs, employees can become active participants in safeguarding the organization’s data assets against both external threats and insider risks.
Data Anonymization
Organizations will inevitably use personally identifiable information (PII) within business operations. Having this data exposed for everyone to read and use is a strict violation of rights.
Overcoming this issue is challenging but not impossible. Using data anonymization to ensure that PII cannot be traced back to an individual significantly reduces the risk of sensitive data exposure.
It is important to keep in mind that most of the time, data anonymization involves the intervention of humans to help classify this sensitive data; this is not an easy process since it is time-consuming and error-prone.
Securing Data with PVML
Now that you know why you should protect sensitive data and the best practices for doing so, it’s important to understand that there are tools available that let you protect your data with ease.
For instance, PVML just so happens to be at the center of helping organizations deal with data in ways that they would have never imagined by clearly asserting their dominance in the data analytics space without compromising data privacy.
Taking a look at some of the key solutions that PVML offers enables organizations to see how effective these solutions are at solving issues that they also might have:
- Data analysis with AI: PVML lets you unlock access to sensitive data using free text without compromising data privacy. So, you’re able to see sensitive data without actually compromising privacy.
- Data anonymization: It’s important to understand that your data is fully available for analysis, but no single record can be observed, reproduced, or extracted, thus ensuring complete anonymity and privacy.
- Data monetization: You can explore business opportunities with third-party clients and monetize your data without risking privacy.
Each of these key areas highlights services that are sought after by most organizations as they try to leverage data for their benefit.
Once organizations collect data as a part of their business processes, they must know how to conduct analysis in a secure way to draw the most out of the data while retaining data privacy.
Take it a step further when you start monetizing this data to bring in more revenue; however, doing this without compromising data privacy is tedious.
So, having a solution such as PVML saves organizations the hassle of architecting and implementing solutions that focus on protecting sensitive data.
Organizations can now use PVML to take their data journey to the next level by signing up for a demo today!
Conclusion
Looking back at how organizations utilize sensitive data for their business processes, proper data protection measures must be implemented. However, implementing these fundamental techniques may not be enough, considering the complex business requirements.
Therefore, utilizing advanced solutions provided by vendors such as PVML makes life easier for businesses attempting to make the most out of the data while respecting the privacy of the data being collected and used.