In today’s data-driven world, protecting personal data and privacy has become paramount. With the proliferation of data breaches and the increasing amount of personal information collected and shared, individuals and organizations are seeking adequate ways to safeguard sensitive data. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on leveraging PET to enhance data privacy and protection, the relationship between data protection and privacy, and practical applications of PET.

Privacy-enhancing technology (PET) has emerged as an important tool to mitigate privacy risks and ensure data confidentiality while maximizing data utility.
Let’s get started;
Understanding Privacy-enhancing technology
Privacy-enhancing technology (PET) is a term that encompasses a range of tools, techniques, and procedures designed to protect and enhance an individual’s confidentiality in the digital age. The main objective of PET is to strike a balance between the need for data sharing and the protection of sensitive information.
According to the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), “PETs are technologies that embody fundamental data protection principles by minimizing personal data use, maximizing data security, and/or empowering individuals. Data Protection law does not define PETs, the concept covers many different technologies and techniques.”
PETs have been around for a decade but have regained popularity because of the rising awareness around security and privacy compliance. You might be familiar with some of them, such as anonymization, homomorphic encryption, synthetic data, or differential privacy. Let’s dive into the details.
Examples of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
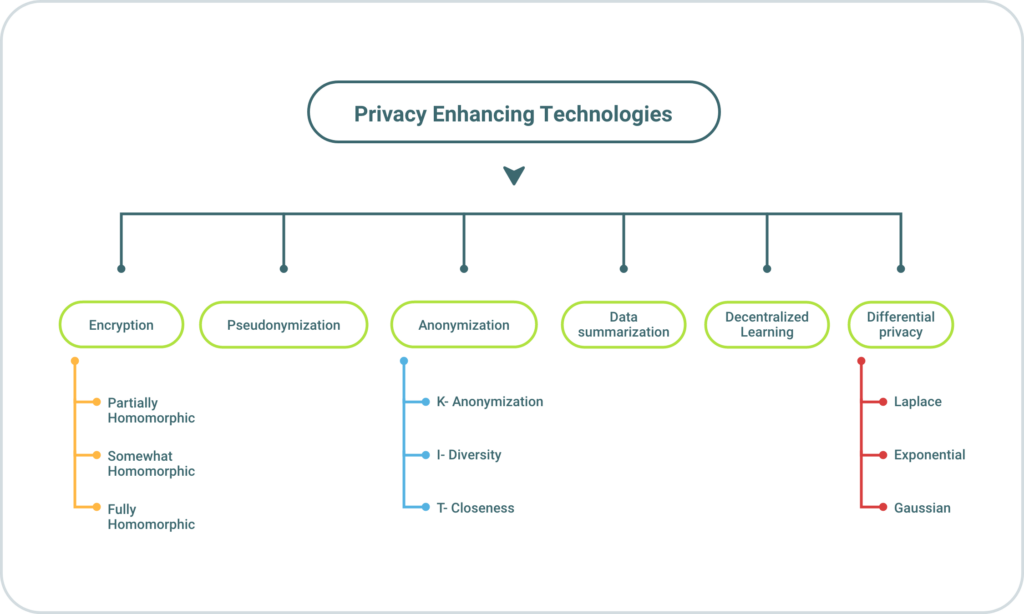
Among PET types, you’ll find:
- Anonymization is the most commonly adopted PET. It’s used in personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets, making it difficult to link data to specific individuals. The most commonly employed method includes k-anonymity, differential privacy, and masking.
- Encryption transforms data into a secure, unreadable format, which can only be decrypted by authorized parties. The main idea of this PET is to collaborate with multiple external, third-party companies or keep data in a cloud environment in a safe and compliant way. Examples of encryption methods are homomorphic encryption, end-to-end encryption, and public-key cryptography.
- Consent management enables individuals to manage how data is collected and used. Consent management tools are extremely important when it comes to ensuring that data processing adheres to privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Privacy-preserving computation allows data analysis without exposing the raw data, ensuring privacy during data processing and analysis.
- Data minimization helps to reduce the amount of collected data to the bare minimum required for a specific purpose, thus limiting the disclosure of sensitive information.
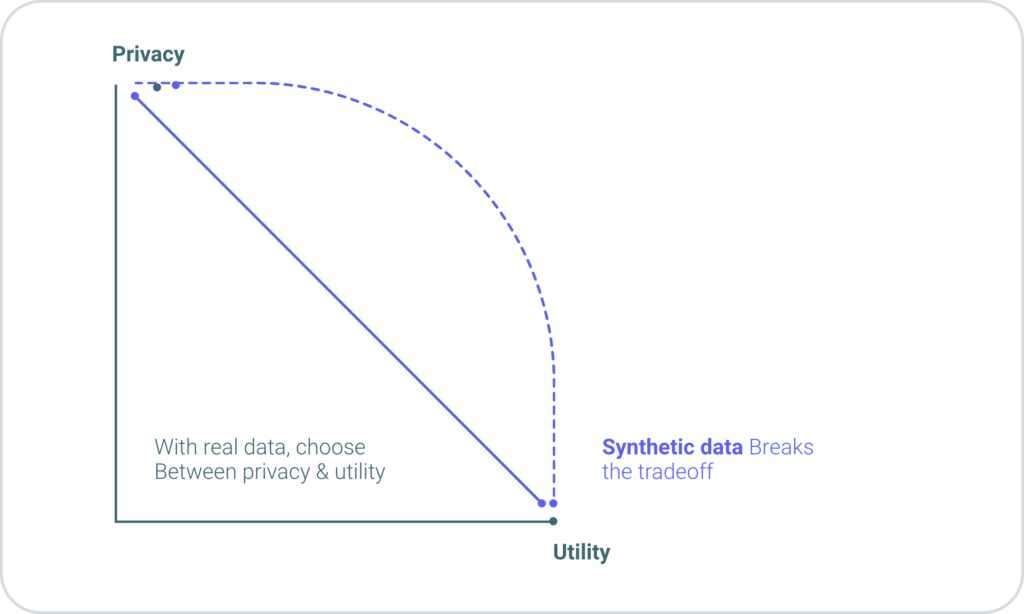
- Synthetic data generation creates artificial data using different algorithms, including ML. Synthetic data is realistic but not real; it mimics real data’s statistical properties without containing a single real person’s information. Therefore, If you are interested in PET because you need to transform your data into a testing environment where third-party users can have access, generating synthetic data that has the same statistical characteristics is a better option. By breaking the one-to-one relationship between a data point and a person, synthetic data makes it impossible to figure out anyone’s private information. Below is a graph that shows the privacy vs. utility tradeoff for real and synthetic data; you can see how synthetic data enables both higher privacy and utility simultaneously:
Selecting a Suitable PETs
Several factors must be put into consideration when selecting the right PETs; here are some tips we’ve put together that will help you in choosing suitable data protection:
| Use case | Recommended PET |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Relationship between data protection and privacy
These two terms are closely related concepts, and they often overlap, but they’re two different things. Let’s explore the relationship between them:
Definition
Data Protection?
This refers to the practices, policies, and measures put in organizations and individuals to protect personal data from unauthorized access, alteration, destruction, and disclosure. In addition, data protection focuses on ensuring the security and integrity of data, and it also involves technical, organizational, and legal measures to curb data breaches and unauthorized data processing.
Data privacy?
On the other hand, data privacy is a wider concept that comprises an individual’s right to control their data and how it’s collected, used, and shared by others. Also, privacy is about an individual’s ability to keep certain aspects of their life and identity confidential. It does not only include the protection of personal data but also the sovereignty and choice of individuals regarding their personal information.
Below is the summary of the relationship between data protection and privacy;
- Data Protection is a subset of privacy and is one of the key instruments used to defend an individual’s right to privacy.
- While data protection primarily focuses on technical and organizational aspects of securing data, privacy goes beyond that and encloses consideration for transparency approval and individual control over personal information.
- Data Protection measures, such as encryption, access control, and data retention policies, are implemented to guarantee that personal data is addressed in a way that respects an individual’s privacy rights.
- Privacy laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, often incorporate provisions for data protection. These laws mandate organizations to enforce data protection measures to protect the personal information they obtain.
- Finally, data protection is a vital component of ensuring privacy. However, privacy is a broader concept that comprises ethical, legal, and cultural aspects beyond data security. Both are paramount in the modern digital age to protect individual rights and personal information while enabling data to be used for legitimate purposes.
The Importance of PET for Data Protection and Privacy
Privacy-enhancing technology (PET) plays a crucial role in protecting data and privacy in several ways, some of which are;
- Legal compliance: In a period of stringent data protection regulations like GDPR, PET helps organizations fulfill their legal responsibilities by providing tools and techniques for securing personal data.
- Minimizing data breach risks: PET reduces the danger of data breaches and unauthorized access through various measures, including anonymizing, encrypting, and applying access controls to data.
- Enhancing ethical data practices: The adoption of PET reveals an organization’s obligation to ethical data handling, which is increasingly important in the eyes of the public.
- Building trust: The use of PET demonstrates a commitment to privacy and data protection, promoting trust with customers, stakeholders, and partners.
- Preserving individual rights: PET empowers individuals by enabling them to manage their data, decide who can have access, and exercise their privacy rights.
Leveraging PET in data protection and privacy
Now, let’s dive deeper into how organizations and individuals can effectively leverage Privacy-Enhancing technologies for data protection and privacy:
Data anonymization
Data anonymization is a basic PET procedure used for protecting personal information. It involves eliminating or replacing PII in datasets, making it difficult to identify individuals. Data anonymization can be carried out effectively by;
- Identifying PII: This technique begins by identifying all the PII in your datasets, including names, phone numbers, email addresses, etc.
- Considering the right anonymization method: Opt for the most adequate anonymization technique for your data, such as suppression, perturbation, or generalization.
- Maintain data utility: While performing data anonymization, always ensure that it remains useful for its intended purpose. Hitting the right balance between anonymity and utility is essential.
- Incessant review and update: Anonymization is a continuous task; therefore, it requires periodic review and update to adapt to changing privacy risks.
Data encryption
Data encryption is regarded as the cornerstone of data protection. As discussed earlier, it ensures that data is secure and only accessible by authorized parties. To leverage encryption effectively,
- Employ strong encryption algorithms: Ensure you implement modern encryption algorithms that are recognized for their resilience and security.
- Protect encryption keys: Protect encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access. Consider hardware security modules (HSMs) for key protection.
- Enforce end-to-end encryption: Consider implementing end-to-end encryption for communication and data storage, as it ensures the encryption of data from the sender to the recipient.
- Monitor and audit encryption: Lastly, you should ensure monitoring and auditing encryption processes to detect any susceptibility or infringements.
Consent Management
Consent management tools are important for organizations that collect and process personal data, and here’s how to leverage them effectively.
- Transparency and user control: Inform individuals about what data is obtained and how it will be used. Allow users to easily give or withdraw approval.
- Data subject access requests: Build processes to handle data subject access requests promptly, allowing individuals to exert their rights under data protection regulations.
- Consent records: Maintain records of approval given, including the specific details of what users consented to. This step is necessary for compliance and Accountability.
- Regular consent audits: Ensure that you review and audit your consent management processes frequently to make sure that they remain useful and in compliance with developing regulations.
Data minimization
Minimizing the amount of data collected will help to limit the risks to privacy. To leverage data minimization effectively, here’s how to go about it.
- Identify data necessity: Always determine the minimum amount of data required for a specific purpose, avoiding the collection of unnecessary information.
- Frequent data purges: Periodic reviewing and deleting of data that are no longer needed reduces the data exposure over time.
- Orientation of employees: Enlightening employees to understand the importance of data minimization and its role in privacy protection will also go a long way.
- Develop data retention policies: Cultivate clear data retention policies that dictate how long different types of data will be maintained.
Privacy-preserving computation
Last on this list is privacy-preserving computation. These techniques enable organizations to analyze data without disclosing sensitive information. You can execute this effectively by;
- Differential privacy: A differential privacy mechanism should be enforced to allow aggregate analysis without revealing individual data. This method is used to protect data by adding noise to the query results, thereby making it difficult to identify individual records. We can use the ‘numpy’ library for a basic example:
import numpy as np # Define the data data = np. array([25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60]) # Define the privacy parameter epsilon = 0.5 # Add Laplace noise to data noisy_data = data + np. random.Laplace(scale=1/epsilon, size=len(data)) # Query the noisy data mean_noisy_data = np. mean(noisy_data) # Reconstruct the query result original_result = mean_noisy_data - np. random.Laplace(scale=1/epsilon)
- Secure multi-party computation(MPC): Implementation of MPC will enable parties to jointly compute results without exposing their inputs.
- Homomorphic encryption is a popular example of encryption that allows computation on encrypted data without decrypting it. This technology allows secure data processing while maintaining privacy. Let’s use the pySEAL library for a Python implementation:
# Install PySEAL using pip pip install seal import seal # Create encryption parameters parms = seal.EncryptionParameters(seal.scheme_type.CKKS) # Set encryption parameters parms.set_poly_modulus_degree(8192) parms.set_coeff_modulus(seal.CoeffModulus.BFVDefault(8192)) parms.set_plain_modulus(seal.PlainModulus(1 << 8)) context = seal.SEALContext.Create(parms) keygen = seal.KeyGenerator(context) public_key = keygen.public_key() secret_key = keygen.secret_key() # Create an encryptor and decryptor encryptor = seal.Encryptor(context, public_key) decryptor = seal.Decryptor(context, secret_key)
- Seek expertise knowledge: Privacy-preserving computation is a complicated technique that might require the knowledge of expertise. Therefore, you should consider consulting with experts or institutions specializing in secure computation.
Practical applications of Privacy-Enhancing technologies (PET)
Here are a few scenarios we’ve compiled for a better understanding of the real-world application of PET. Let’s explore ;
- Healthcare data protection: The usefulness of PET in the healthcare sector cannot be overemphasized. It plays a vital role in anonymizing patient records, securing medical communications, and enabling research through privacy-preserving computation. Also, techniques like securing multi-party computation allow hospitals to collaborate on medical research without disclosing sensitive patient data.
- Financial data security: Financial institutions such as banks, brokerage firms, etc rely on PET to protect customer financial information. Encryption is broadly used in online banking, and data minimization ensures that only necessary financial information is obtained.
- Secure messaging and video conferencing: Privacy-enhancing technology is used in secure messaging and video conferencing tools to safeguard the privacy of communications, most especially in sensitive or confidential contexts.
- Smart devices and IoT: PET can be incorporated into IoT devices to protect user’s data and prevent unauthorized access to smart home systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, leveraging Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PET) is indispensable for robust data protection and privacy. By implementing PET solutions such as encryption, anonymization, and access controls, individuals and organizations can mitigate the threats of data breaches and unauthorized access. PET not only safeguards sensitive information but also ensures compliance with privacy regulations. With the increasing importance of data privacy in today’s digital landscape, it is imperative to take on PET as a fundamental aspect of data protection strategies. By prioritizing PET, we can nurture a secure and trustworthy environment for data management.